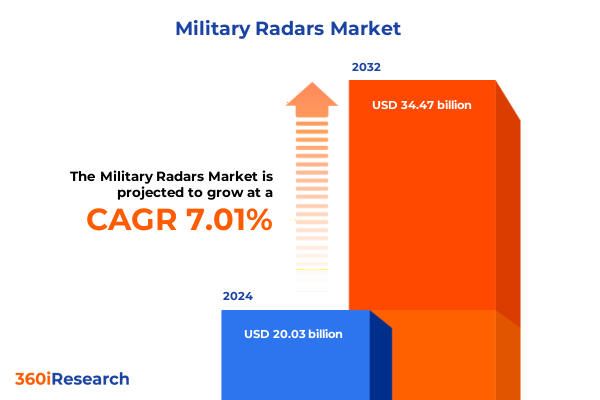
The Military Radars Market size was estimated at USD 17.57 billion in 2025 and expected to reach USD 18.64 billion in 2026, at a CAGR of 7.19% to reach USD 28.59 billion by 2032.
Comprehensive Overview of Military Radar Ecosystems Highlighting Strategic Imperatives Driving Modern Defense Sensor Architecture and Operational Readiness
The global defense landscape is witnessing an unprecedented acceleration in the evolution of radar systems driven by emerging threats and rapid technological advancement. Over the past decade, conflicts have demonstrated the criticality of real-time situational awareness, prompting defense organizations to prioritize sensor performance and interoperability. This executive summary opens with a comprehensive overview of how modern military radar architectures are being reimagined to address high-altitude aerial incursions, low-observable stealth platforms, and proliferating unmanned systems.
Market participants are leveraging advances in signal processing, software-defined hardware, and network integration to optimize detection ranges, resolution, and multi-target tracking accuracy. As defense budgets stabilize in key regions, procurement strategies increasingly favor modular, upgradeable radar solutions that can be integrated into legacy platforms while supporting future capability expansions. The convergence of electronic warfare resilience, spectrum agility, and intelligent automation is reshaping design priorities, urging suppliers and end users alike to reevaluate core operational requirements.
Drawing upon primary interviews with system integrators, radar engineers, and procurement officers, this section sets the stage for a deeper exploration of transformative shifts, tariff impacts, segmentation nuances, regional dynamics, competitive frameworks, and actionable recommendations. It establishes the foundational context necessary for decision-makers to navigate complex trade-offs between cost, performance, and strategic alignment within the evolving military radar domain.
Key Transformative Shifts Redefining Military Radar Capability Through Technological Innovation Digital Integration and Network-Centric Warfare Strategies
Over the past five years, several pivotal shifts have redefined the trajectory of military radar development, driven by breakthroughs in digital electronics, network-centric doctrines, and artificial intelligence. First, the integration of software-defined radar architectures has empowered operators to modify waveforms, switch frequency bands, and implement counter-countermeasures remotely without hardware changes. This flexibility has become a cornerstone for multi-domain operations, allowing seamless handoffs between airborne early warning and ground-based missile defense systems.
Concurrently, the rise of active electronically scanned arrays (AESA) has revolutionized beam steering and target engagement timelines, enabling simultaneous multi-mission execution with heightened resistance to jamming and interference. In parallel, advances in data fusion and machine learning algorithms are enabling real-time classification and threat prioritization across disparate sensor inputs. These capabilities are being fielded within distributed networks that link shipborne combat platforms, land-based installations, and space-based assets, forging a unified battlespace picture.
Moreover, the growing adoption of unmanned aerial systems equipped with compact, low-power radars is introducing new considerations for system resilience and spectrum management. As defense stakeholders pivot toward integrated lethality, they are prioritizing open architectures, modular upgrades, and vendor-agnostic interfaces to future-proof investments. These transformative shifts underscore the imperative for industry leaders to innovate rapidly while ensuring interoperability across legacy and next-generation platforms.
Comprehensive Analysis of the Cumulative Impact of United States Tariff Measures in 2025 on Military Radar Supply Chains Costs and Technological Collaboration
In early 2025, the United States implemented a new tranche of tariffs targeting key semiconductor components, composite materials, and advanced electronic subassemblies used in military radar production. These measures were designed to bolster domestic industry resilience but have had multifaceted ripple effects on the global supply chain. Suppliers in allied nations are grappling with increased input costs, leading to renegotiations of contracts, adjusted lead times, and strategic relocations of manufacturing capacity to mitigate tariff exposure.
The immediate consequence has been a recalibration of total acquisition costs for radar upgrades, compelling end users to phase procurement cycles and prioritize incremental capability enhancements over large-scale platform overhauls. Simultaneously, several original equipment manufacturers have accelerated partnerships with domestic foundries and material suppliers, seeking tariff exemptions through special tariff engineering and localization initiatives. This shift toward onshore production has reinforced sovereign industrial base objectives but introduced challenges in scaling output and maintaining quality standards.
Looking ahead, technology collaboration frameworks between the U.S. and allied defense sectors are evolving to streamline shared R&D investments and co-production agreements. These arrangements aim to distribute tariff risks while preserving strategic interoperability. As a result, industry stakeholders are adopting hybrid sourcing strategies, combining domestic manufacturing with diversified global suppliers in tariff-exempt jurisdictions to ensure stable component availability and cost containment in the wake of 2025’s tariff landscape.
Deep Dive into Military Radar Market Segmentation Across Type Application Platform Frequency Band and Technology Innovations Driving Custom Solutions
The military radar market can be dissected by type, application, platform, frequency band, and technology, each revealing opportunities for tailored solutions. By type, radar systems span airborne early warning and control, air surveillance, and fire control variants for aerial platforms, while ground installations range from fixed installations at strategic facilities to mobile radars mounted on armored vehicles. Naval radar offerings include shipborne combat suites optimized for target tracking and shipborne navigation radars for safe maneuvering at sea, and space-based sensors extending coverage to orbital domains.
Applications further delineate systems designed for civil-military air traffic control, artillery fire control subdivisions encompassing both air defense and artillery fire control scenarios, and a broad suite of surveillance and reconnaissance radars that monitor air, ground, and maritime theaters. Target acquisition capabilities specialize in anti-tank guided missile detection and ballistic missile tracking, whereas weather monitoring radars support both tactical and humanitarian missions.
Platform segmentation underscores the criticality of form factor in mission planning: airborne radars mounted on fighter jets and surveillance aircraft; fixed installations securing base perimeters; portable systems rapidly deployable by expeditionary forces; shipborne arrays safeguarding naval task groups; and vehicle-mounted radars enhancing land maneuver units. Frequency band choices from C, Ka, Ku, L, S to X band dictate resolution, range, and atmospheric penetration trade-offs. Finally, technology archetypes such as continuous wave, frequency-modulated continuous wave, phased array-active and passive electronically scanned array-and pulse Doppler variants with high and medium pulse repetition frequencies, alongside synthetic aperture radar, shape performance envelopes based on mission requirements and environmental constraints.
This comprehensive research report categorizes the Military Radars market into clearly defined segments, providing a detailed analysis of emerging trends and precise revenue forecasts to support strategic decision-making.
- Type
- Frequency Band
- Technology
- Application
Strategic Regional Dynamics and Key Defense Radar Developments Shaping Growth Prospects in the Americas Europe Middle East Africa and Asia Pacific
Regional dynamics within the military radar market are characterized by distinct procurement drivers and industrial capabilities. In the Americas, the United States leads modernization programs focused on long-range early warning, integrated air and missile defense, and allied interoperability initiatives. Canadian and Latin American forces are pursuing cost-effective upgrades emphasizing mobility and multirole versatility to address diverse domestic security challenges.
Europe, the Middle East, and Africa constitute a heterogeneous landscape where NATO member states prioritize networked ground-based radars and naval sensor integration, while Gulf Cooperation Council nations invest aggressively in next-generation naval and airborne systems. African defense budgets, though constrained, are allocating resources toward mobile surveillance radars to counter asymmetric threats and support border security operations.
Asia-Pacific exhibits rapid expansion driven by maritime domain awareness requirements, territorial dispute pressures, and high-tempo aerial threats. Major powers in the region are expanding indigenous radar R&D, while smaller nations seek turnkey solutions through offset agreements. Australia’s emphasis on layered air defense, India’s push for domestic phased array capabilities, and Southeast Asian coastal surveillance programs collectively underscore a robust appetite for diversified radar portfolios tailored to regional mission sets.
This comprehensive research report examines key regions that drive the evolution of the Military Radars market, offering deep insights into regional trends, growth factors, and industry developments that are influencing market performance.
- Americas
- Europe, Middle East & Africa
- Asia-Pacific
In-Depth Corporate Strategies and Technological Leadership of Leading Defense Radar Suppliers Driving Competitive Advantage Through Innovation Partnerships
Leading defense contractors are actively shaping the military radar arena through targeted investments, strategic partnerships, and technology acquisitions. One prominent supplier has leveraged its extensive R&D infrastructure to refine active electronically scanned array modules, securing key contracts for next-generation airborne early warning platforms. Another major integrator has formed joint ventures with international electronics firms to co-develop software-defined radar cores, accelerating time to field while mitigating geopolitical supply risks.
Several established players are diversifying their portfolios by acquiring niche specialists in synthetic aperture radar and counter-drone detection systems, aiming to offer end-to-end sensor suites compatible with both legacy and emerging platforms. Meanwhile, some companies are consolidating through mergers to achieve economies of scale in ground-based missile defense radars, positioning themselves as prime vendors for multi-national procurements. Partnerships between prime contractors and small-enterprise innovators are also fostering breakthrough developments in low-observable radar signature management and cognitive electronic warfare resilience.
These corporate strategies are anchored by commitments to lifecycle support, digital twin simulations, and modular hardware upgrade paths. By aligning roadmaps with evolving defense doctrines, suppliers are not only maintaining competitive positioning but also facilitating seamless capability insertion for armed forces navigating budget constraints and complex interoperability demands.
This comprehensive research report delivers an in-depth overview of the principal market players in the Military Radars market, evaluating their market share, strategic initiatives, and competitive positioning to illuminate the factors shaping the competitive landscape.
- Airbus SE
- BAE Systems plc
- Bharat Electronics Limited
- Elbit Systems Ltd.
- General Dynamics Corporation
- Hensoldt GmbH
- Honeywell International Inc.
- Israel Aerospace Industries Ltd.
- L3Harris Technologies, Inc.
- Leonardo S.p.A.
- Lockheed Martin Corporation
- Mitsubishi Electric Corporation
- Northrop Grumman Corporation
- Raytheon Technologies Corporation
- Saab AB
- Thales S.A.
Strategic Actionable Recommendations for Defense Industry Leaders to Enhance Military Radar Effectiveness Foster Innovation and Strengthen Supply Chain Resilience
Industry leaders should prioritize the adoption of open architecture frameworks to ensure that radar subsystems can be upgraded rapidly in response to emerging threats without incurring prohibitive recertification costs. Equally critical is the investment in cross-domain digital twins that simulate radar performance under varied environmental conditions and electronic warfare scenarios, thereby shortening development cycles and validating system resilience before deployment.
To strengthen supply chain resilience in the face of tariff disruptions, organizations should diversify component sourcing by establishing dual-track procurement pipelines within allied jurisdictions while nurturing strategic relationships with domestic suppliers. This hybrid approach mitigates the risk of single-source dependencies and supports sovereign defense industrial base objectives.
Collaborative R&D consortia between governments, OEMs, and academic institutions can accelerate breakthroughs in machine learning-enabled signal processing and next-gen sensor fusion. By sharing pre-competitive research outcomes, stakeholders can drive down individual program costs while expanding the collective technology frontier. Furthermore, fostering a skilled workforce through joint training programs with system integrators and defense academies will ensure that end users can exploit advanced radar capabilities fully from initial fielding to operational sustainment.
Rigorous Research Methodology Employing Primary Expert Interviews Secondary Data Triangulation and Quantitative Analysis for Military Radar Market Insights
This study employed a two-pronged research methodology combining primary expert engagements with comprehensive secondary data analysis. Primary research included in-depth interviews with radar system engineers, procurement officials, and industry executives across North America, Europe, and Asia-Pacific to capture nuanced insights into program requirements, technology preferences, and vendor selection criteria.
Secondary research entailed systematic reviews of open-source defense publications, government procurement records, regulatory filings, and academic journals covering radar signal processing, electronic warfare, and aerospace systems. Data triangulation techniques were applied to reconcile discrepancies between projected capability roadmaps and actual contract awards, ensuring the reliability of trend assessments.
Quantitative analysis was conducted on published equipment inventories, defense budget allocations, and announced R&D expenditures, while qualitative assessments evaluated strategic white papers, defense policy frameworks, and industry consortium outputs. Validation workshops with former radar program leads and technical subject matter experts provided critical feedback loops, refining the study’s conclusions and reinforcing confidence in the strategic recommendations presented herein.
This section provides a structured overview of the report, outlining key chapters and topics covered for easy reference in our Military Radars market comprehensive research report.
- Preface
- Research Methodology
- Executive Summary
- Market Overview
- Market Insights
- Cumulative Impact of United States Tariffs 2025
- Cumulative Impact of Artificial Intelligence 2025
- Military Radars Market, by Type
- Military Radars Market, by Frequency Band
- Military Radars Market, by Technology
- Military Radars Market, by Application
- Military Radars Market, by Region
- Military Radars Market, by Group
- Military Radars Market, by Country
- United States Military Radars Market
- China Military Radars Market
- Competitive Landscape
- List of Figures [Total: 16]
- List of Tables [Total: 2067 ]
Strategic Conclusion Summarizing Key Radar Market Trends Technological Drivers and Regional Dynamics Informing Future Defense Sensor Investment Decisions
In summary, the military radar domain is undergoing a profound transformation driven by digital architectures, spectrum-agile designs, and integrated sensor networks. Technological innovations such as active electronically scanned arrays, cognitive signal processing, and machine learning-enabled threat classification are elevating system effectiveness across airborne, ground, naval, and space applications.
Regional defense priorities and budgetary imperatives are shaping procurement strategies, with the Americas focusing on interoperability and sovereign supply chain resilience, Europe, Middle East, and Africa balancing modernization with cost efficiency, and Asia-Pacific pursuing scale and indigenous capability development. Major industry players are forging partnerships and executing targeted acquisitions to maintain competitive differentiation in this dynamic market.
As defense stakeholders navigate tariff-induced supply challenges and evolving threat landscapes, adherence to open standards, investment in digital twin simulations, and diversification of manufacturing footprints will be critical. The insights and recommendations detailed in this executive summary equip decision-makers with the strategic foresight needed to optimize radar system investments, accelerate capability deployment, and ensure operational superiority in contested environments.
Call to Action Engage with Associate Director Ketan Rohom to Acquire the Comprehensive Military Radar Market Research Report to Empower Strategic Growth
To explore these in-depth insights and gain a competitive edge in military radar procurement and deployment, reach out today. Contact Ketan Rohom, Associate Director Sales & Marketing, who can provide a detailed overview of the full research deliverable, including strategic imperatives, technology forecasts, and supplier evaluations. Secure your copy of this indispensable military radar market intelligence to guide your next strategic choices and operational decisions.

- How big is the Military Radars Market?
- What is the Military Radars Market growth?
- When do I get the report?
- In what format does this report get delivered to me?
- How long has 360iResearch been around?
- What if I have a question about your reports?
- Can I share this report with my team?
- Can I use your research in my presentation?




